Table of Contents
For evaluating and ranking potential investment opportunities and business projects, the internal rate of return is one important metric that businesses and individuals use for financial analysis.
This article covers the meaning of internal rate of return, the IRR formula, how to calculate internal rate of return, when it’s used, and FAQs.
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
Internal rate of return is a capital budgeting calculation for deciding which projects or investments under consideration are investment-worthy and ranking them. IRR is the discount rate for which the net present value (NPV) equals zero (when time-adjusted future cash flows equal the initial investment). IRR is an annual rate of return metric also used to evaluate actual investment performance.
Understanding IRR
IRR is computed using a different type of discounted cash flow analysis to determine the rate that produces the initial investment breakeven. The initial investment is the company’s cost to launch the investment project.
Businesses compare the internal rate of return (IRR) for potential projects. When evaluating potential investment options, they often choose the highest IRR expected return that meets or exceeds the minimum percentage hurdle rate required for company investments.
If the budget amount is large enough for investment in more than one project, then available funds are allocated to other higher IRR projects within the company’s budget and risk tolerance.
Basic cash flow analysis is analyzing the cash inflows and outflows that are presented in a cash flow statement.
The corporate hurdle rate equals their weighted-average cost of capital (WACC), including a risk premium. A company’s WACC is the weighted average of its costs of equity, debt, and preferred stock, according to Strategic CFO.
A Harvard Business Review article about Internal Rate of Return (IRR) recommends that IRR be used in combination with net present value (NPV) to make better investment decisions. In a net present value financial analysis, a positive NPV means investment profitability.
In corporate finance, venture capital firms and private equity investment companies use cash-on-cash return or internal rate of return as methods to analyze which startups and growth companies they should fund as portfolio investments. Commercial real estate investors use IRR to evaluate potential or actual returns on investment properties.
Individuals may also use IRR to make personal investments and major purchasing decisions that can generate returns, such as an annuity.
Internal Rate of Return Formula
The internal rate of return (IRR) formula is based on the net present value (NPV) formula when it’s used to solve for zero NPV.
The internal rate of return formula is:

How to Calculate IRR
Financial analysts may use mathematical formulas to calculate IRR on a trial-and-error basis by calculating the net present value (NPV) of each cash flow amount, using an estimate of the internal rate of return. A more efficient process is to use three Excel spreadsheet functions for IRR, including IRR, XIRR, and MIRR, according to the Journal of Accountancy.
Instead, you can use a financial calculator for IRR. A financial calculator may either be a physical device with an IRR button (like a specialized Texas Instruments financial calculator) or an online financial calculator for internal rate of return. If you decide to use an online calculator, initially compare the results to Excel to prove its accuracy.
Each Microsoft Excel function formula has certain built-in assumptions and variables to insert. For Excel to work in calculating the three IRR functions, the series of cash flows must include at least one negative cash flow amount for net cash outflows and one positive cash flow amount for net cash inflows.
IRR Function in Excel
The IRR function in Excel assumes periodic cash flows. IRR assumes an equal number of days in monthly cash flow periods. This doesn’t reflect the monthly fluctuations in calendar days for a month, resulting in a small amount of IRR calculation inaccuracy. In Excel, for the IRR function, you can compute IRR using either monthly or annual amounts and choose whether to use a guess.
Calculate IRR as of a certain number of years (or months). In the IRR function, enter the row and column identifiers as a sum for the years being considered in your IRR calculation. If you’re making a guess, that’s an extra entry in the function formula.
Steps for using Excel’s IRR function:
- Click the fx function in Excel.
- Select Financial function.
- In the function search box, type in IRR for the IRR function (and select IRR if given a choice of which IRR function to use).
- Using the Formula Arguments screen, insert the Excel data range as Values for the IRR period being analyzed, and optionally, your guess of the IRR rate.
In the Example of IRR section below, which includes cash flow assumptions, Excel calculates IRR as 16% over a five-year time horizon.
XIRR Function in Excel
The XIRR function in Excel doesn’t need periodic cash flows and uses cash flow dates (using the Excel DATE function or dates in Excel cells formatted as DATE) instead. However, you can use periodic dates. Like IRR, XIRR lets the Excel user optionally insert a guess into the Function Arguments screen box.
Steps for using Excel’s XIRR function:
- Click the fx function in Excel.
- Select Financial function.
- In the function search box, type in XIRR for this type of IRR function (or select XIRR if given a choice of which IRR function to use).
- Using the Formula Arguments screen, insert the Excel data range as Values for the IRR period being analyzed, enter the range of the date cells that have been formatted as DATE, and optionally, your guess of the IRR rate.
Using the same assumptions in the Example of IRR section below, except replacing Years with actual cash flow dates that are in a new column C, the XIRR solves XIRR as 14%.
Excel column C includes the following dates and cell addresses to use in connection with the Example of IRR assumptions data instead of Year number. Cash flows are assumed to remain the same.
| Cell Dates of Cash Flows | Excel Cell Formatted as DATE |
| 2-Jan-17 | C2 |
| 15-Jan-18 | C3 |
| 25-Mar-19 | C4 |
| 16-Feb-20 | C5 |
| 22-May-21 | C6 |
| 28-Dec-22 | C7 |
The XIRR function calculation shows in Excel as XIRR(B2:B7,C2:C7) or XIRR(B2:B7,C2:C7,.11) with an 11% guess. The calculated XIRR appears as 14% and these formulas appear in the cell content bar near the top of the Excel spreadsheet if you click on the 14% result.
MIRR Function in Excel
MIRR is a modified internal rate of return. The MIRR function in Excel uses periodic cash flows (like the IRR function ) and also assumes the reinvestment of cash in the calculation. The MIRR Excel function includes Function Arguments for Values, Finance_rate and Reinvest_rate, but no expected IRR rate guess. The Finance_rate is the interest rate paid on amounts borrowed to finance cash flows. The Reinvest_rate is the interest rate for interest received when money is reinvested from cash flows produced from the investment project.
Steps for using Excel’s MIRR function:
- Click the fx function in Excel.
- Select Financial function.
- In the function search box, type in MIRR for this type of IRR function (or select MIRR if given a choice of which IRR function to use).
- Using the Formula Arguments screen, insert the Excel data range as Values of cash flows for the IRR period being analyzed, and enter the Finance_rate and Reinvest_rate.
Assume the Finance_rate is 8% and the Reinvest_rate is 12%. Using the same cash flow and timing assumptions in the Example of IRR section below, the Excel function solves MIRR as 15%.
When you click on the 15% for MIRR function results, you’ll see MIRR(B2:B7,.08,.12) in the Excel cell content bar.
When to (and Why) Use IRR?
Use IRR (internal rate of return) to evaluate and compare the returns of business investment projects to select the best investment from these competing projects. Businesses often select investment projects with the highest return within their risk appetite that meets their minimum hurdle rate for investing. Individuals can also use IRR for investing.
You can also use IRR to determine the return rate on actual investments when NPV is zero, using discounted cash flow analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
The answers to frequently asked questions about internal rate of return (IRR) follow.
What’s Considered a Good IRR?
A good IRR depends on the industry and the riskiness of the project. Higher-risk projects require greater IRR returns. Businesses select projects with an internal rate of return exceeding their minimum hurdle rate return, which is equal to or exceeding its weighted-average cost of capital (WACC). In real estate, a good IRR may vary from 12% to 20%, depending on the risk level.
What’s an IRR of 30% Mean?
An IRR of 30% means that the rate of return on an investment using projected discounted cash flows will equal the initial investment amount when the net present value (NPV) is zero. In this case, when the time value of money factors are applied to the cash flows, the resulting IRR is 30%. The investment is at breakeven with a 30% IRR.
What’s an Example of IRR?
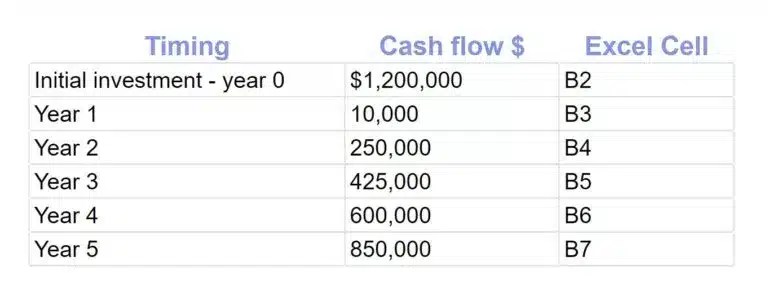
An example of using the IRR function in Excel includes the following assumptions:
Hurdle rate as an optional guess: 11%
WACC: 8%
For a timeframe of five years, Excel shows the IRR function as:
IRR(B2:B7) with no IRR guess or IRR (B2:B7,.11) with a guess of 11% for IRR.
Result: For the above example, IRR = 16%
In this example, over five years, this project returns an IRR of 16%, which is above the company’s 11% hurdle rate for a minimum investment return. If it’s the only project being considered, select the project. If other investment projects are being considered by the business, rank them for the highest IRR above the hurdle rate, but consider other factors, including length of the business investment project, riskiness, and the investment amount required.
What’s the Difference Between IRR and ROI?
ROI (return on investment) considers the cash flows produced over the entire investment life at its end vs. the initial investment. In contrast, IRR (internal rate of return) is an annualized return based on discounting back cash flows for each year for the time value of money. IRR is the rate where the net present value (NPV) is zero.
Importance of Internal Rate of Return
Internal rate of return is an important method for analyzing and selecting business projects or other investments. The advantage of internal rate of return is that businesses will not choose projects estimated to generate a return below their hurdle rate (required rate of return) which includes a risk premium. With internal rate of return, the riskiness of a project is considered in combination with the potential investment’s annual growth rate.
Decisions using internal rate of return should also consider calculations of net present value (NPV), which indicates the estimated discounted cash flow amount exceeding the initial investment. IRR only indicates an annualized percentage return for a period of time (considering the time value of money)rather than a total return amount.
